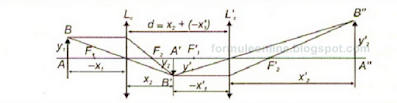
A converging lens (f1 = 20 cm) and another converging lens (f2 = 10 cm) are arranged coaxially at a distance of d = 50 cm one from another. On the left of the first convergent lens at distance (- x) = 60 cm it is an object with height Y1 = 5 cm . Where is formed the final image? What nature and what height has the image?
Solution
The image of the object in the first lens is formed at a distance:
$$x_{2} = \frac{f_{1}x_{1}}{f_{1} + x_{1}} = 30 cm$$
compared to this, in her right side is a real image, inverted and smaller than object AB because:
$$β_{1} = \frac{x_{2}}{x_{1}} = - 0,5$$
This image becomes object for the second lens placed at:
$$x'_{1} = x_{2} - d = - 20 \ cm$$
Since A'B' is located on the left side of the second convergent lens, is becomes real object to it:
$$x'_{2} = \frac{f_{2}x'_{1}}{f_{2} + x'_{1}} = 20 \ cm$$
$$β'_{2} = \frac{x'_{2}}{x'_{1}} = - 1$$
$$β'_{sistem} = β_{1} \cdot β_{2} = 0,5$$
$$y'_{2} = 2,5 \ cm$$
Niciun comentariu:
Trimiteți un comentariu